Why is a concave mirror called converging mirror and convex mirror
Definition of Concave Mirror. Concave mirrors are converging mirrors. The parallel incident rays fall on the mirror's surface and the rays reflect and meet at a certain point known as the focal point.. Answer 1: Convex mirrors are diverging mirrors whereas concave mirrors are converging mirrors. Question 2: Which mirror is used in.

Why is a concave mirror called a converging mirror ? Explain with
DEIB in STEM Ed. Donate. How does a lens or mirror form an image? See how light rays are refracted by a lens or reflected by a mirror. Observe how the image changes when you adjust the focal length of the lens, move the object, or move the screen.
PPT Optics PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID9367240
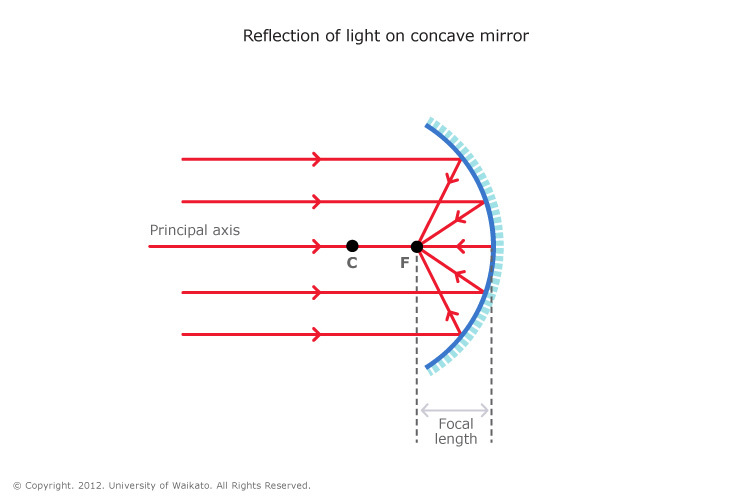
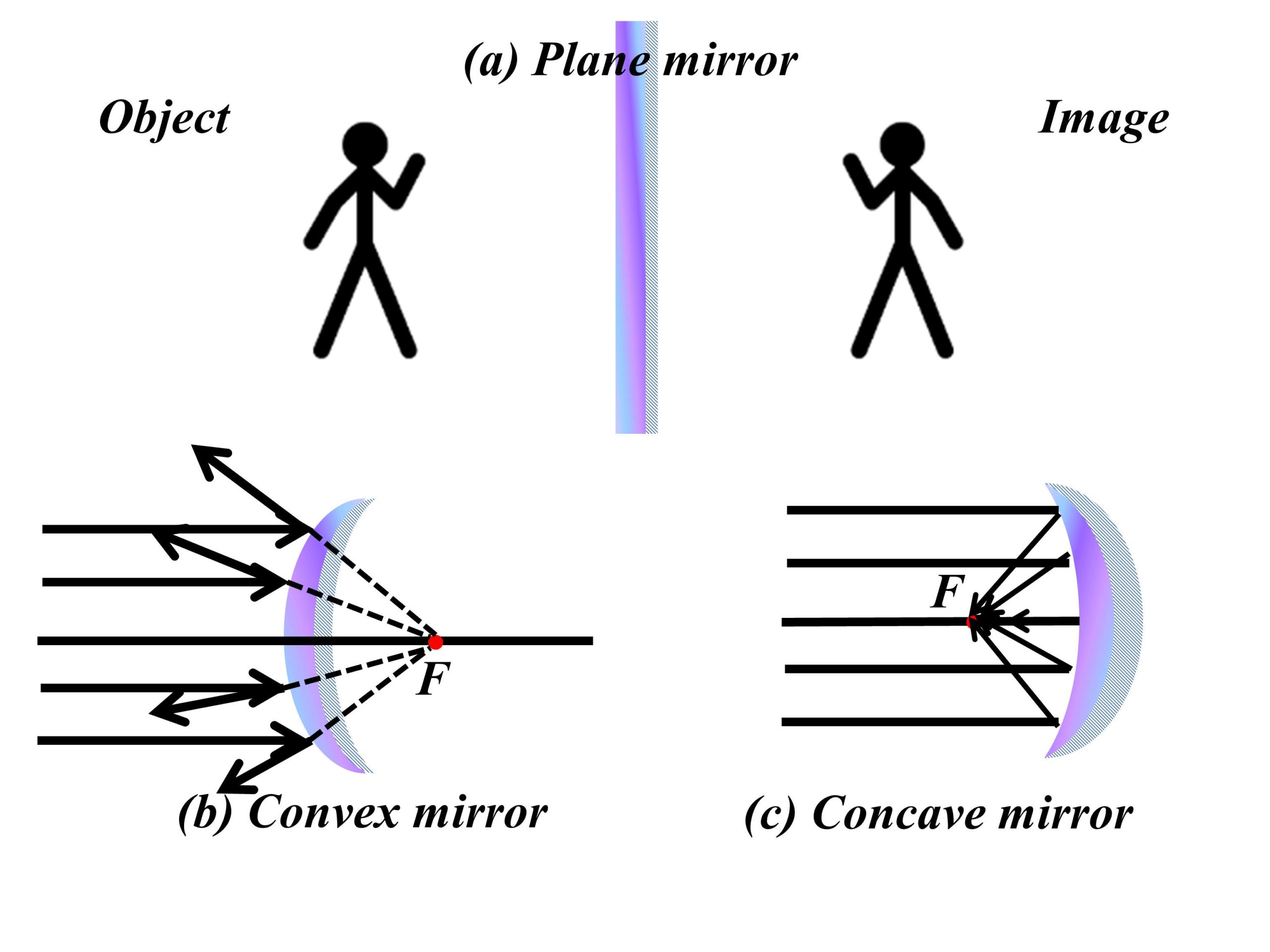
The focal length f of a concave mirror is positive, since it is a converging mirror. Figure 25.39 (a) Parallel rays reflected from a large spherical mirror do not all cross at a common point. (b) If a spherical mirror is small compared with its radius of curvature, parallel rays are focused to a common point.
Rules for drawing Ray Diagram in Convex and Concave Lens Teachoo
Figure 25.6.5: Thin lenses have the same focal length on either side. (a) Parallel light rays entering a converging lens from the right cross at its focal point on the left. (b) Parallel light rays entering a diverging lens from the right seem to come from the focal point on the right.
Explain the rules of concave and convex mirror
Lesson 3 focused on the reflection of light by concave mirrors and on the formation of images by this reflected light. In that lesson, it was shown that concave mirrors can produce both real and virtual images, depending upon the object location.In Lesson 4, we will follow a similar pattern of inquiry for convex mirrors: investigating how convex mirrors reflect light and produce images.

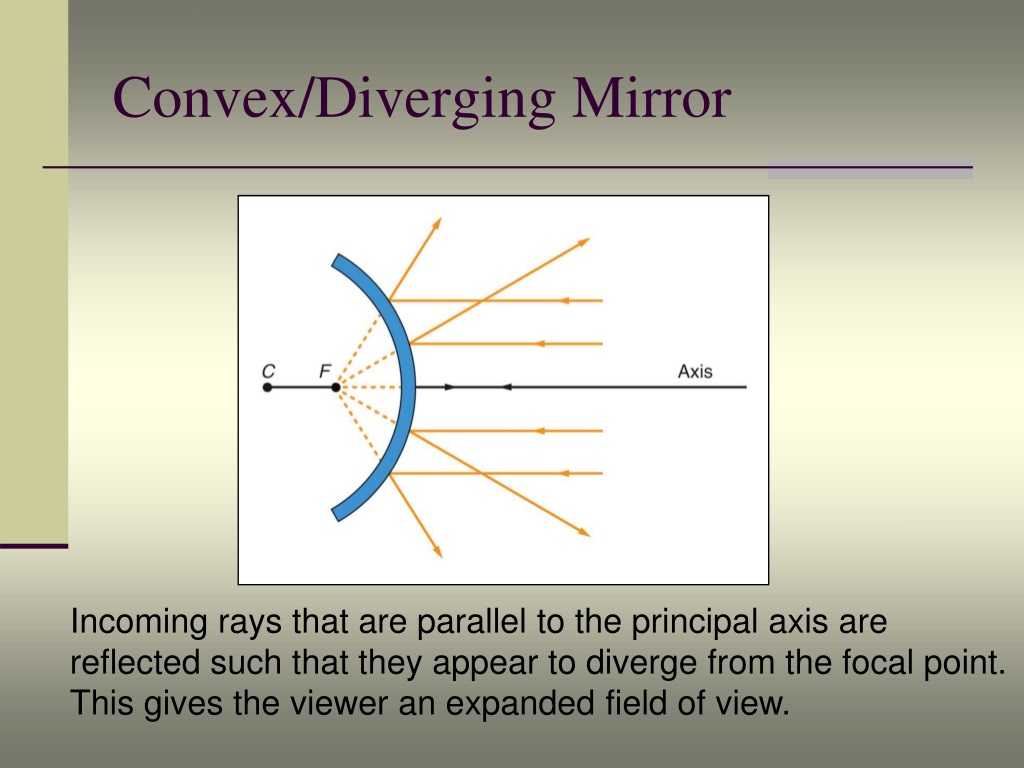
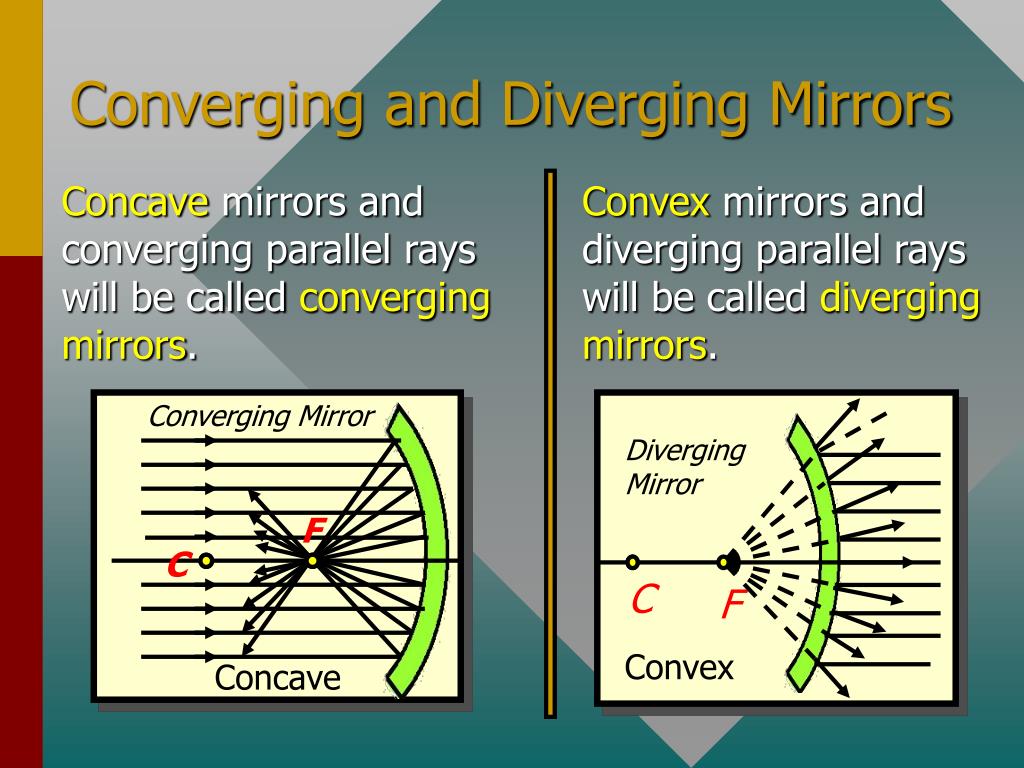
Converging Mirror And Diverging Mirror
Figure 25.26 Sunlight focused by a converging magnifying glass can burn paper. Light rays from the sun are nearly parallel and cross at the focal point of the lens. The more powerful the lens, the closer to the lens the rays will cross. The greater effect a lens has on light rays, the more powerful it is said to be.

Convex And Concave Mirrors And Lenses
The method is applied to the task of drawing a ray diagram for an object located beyond the center of curvature (C) of a concave mirror. Yet the same method works for drawing a ray diagram for any object location. 1. Pick a point on the top of the object and draw two incident rays traveling towards the mirror.
Concave mirror — Science Learning Hub
A ray approaching a concave converging mirror parallel to its axis is reflected through the focal point F of the mirror on the same side. (See rays 1 and 3 in Figure \(\PageIndex{2}\)) A ray approaching a convex diverging mirror parallel to its axis is reflected so that it seems to come from the focal point F behind the mirror.
PPT Chapter 34B Reflection and Mirrors II (Analytical) PowerPoint
A convex mirror diverges light, as does a concave lens. Any lens that is thicker in the center than the ends is a convex lens. Any lens thicker at the ends than in the center is a concave lens. Similarities between lenses and mirrors. The equations we used for mirrors all work for lenses. A convex lens acts a lot like a concave mirror.
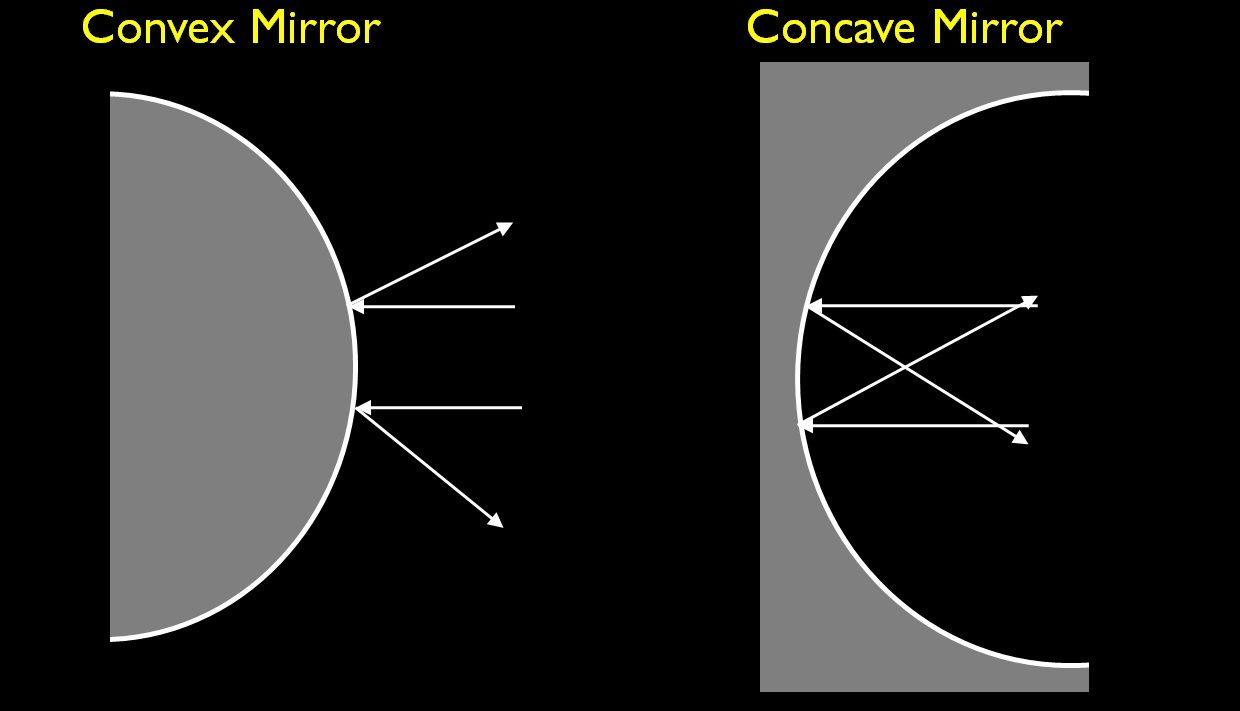
Describe Two Common Uses of a Diverging Mirror
Principal Ray 1: a ray approaching a concave converging mirror parallel to its axis is reflected through the focal point F of the mirror on the same side. (See rays 1 and 3 in Figure \(\PageIndex{2}\)(b).); a ray approaching a convex diverging mirror parallel to its axis is reflected so that it seems to come from the focal point F behind the.
Describe Two Common Uses of a Diverging Mirror
A ray approaching a concave converging mirror parallel to its axis is reflected through the focal point F of the mirror on the same side. (See rays 1 and 3 in Figure 2(b).) A ray approaching a convex diverging mirror parallel to its axis is reflected so that it seems to come from the focal point F behind the mirror. (See rays 1 and 3 in Figure 3.)

Concave Mirror Converging or Diverging SloaneecPerkins
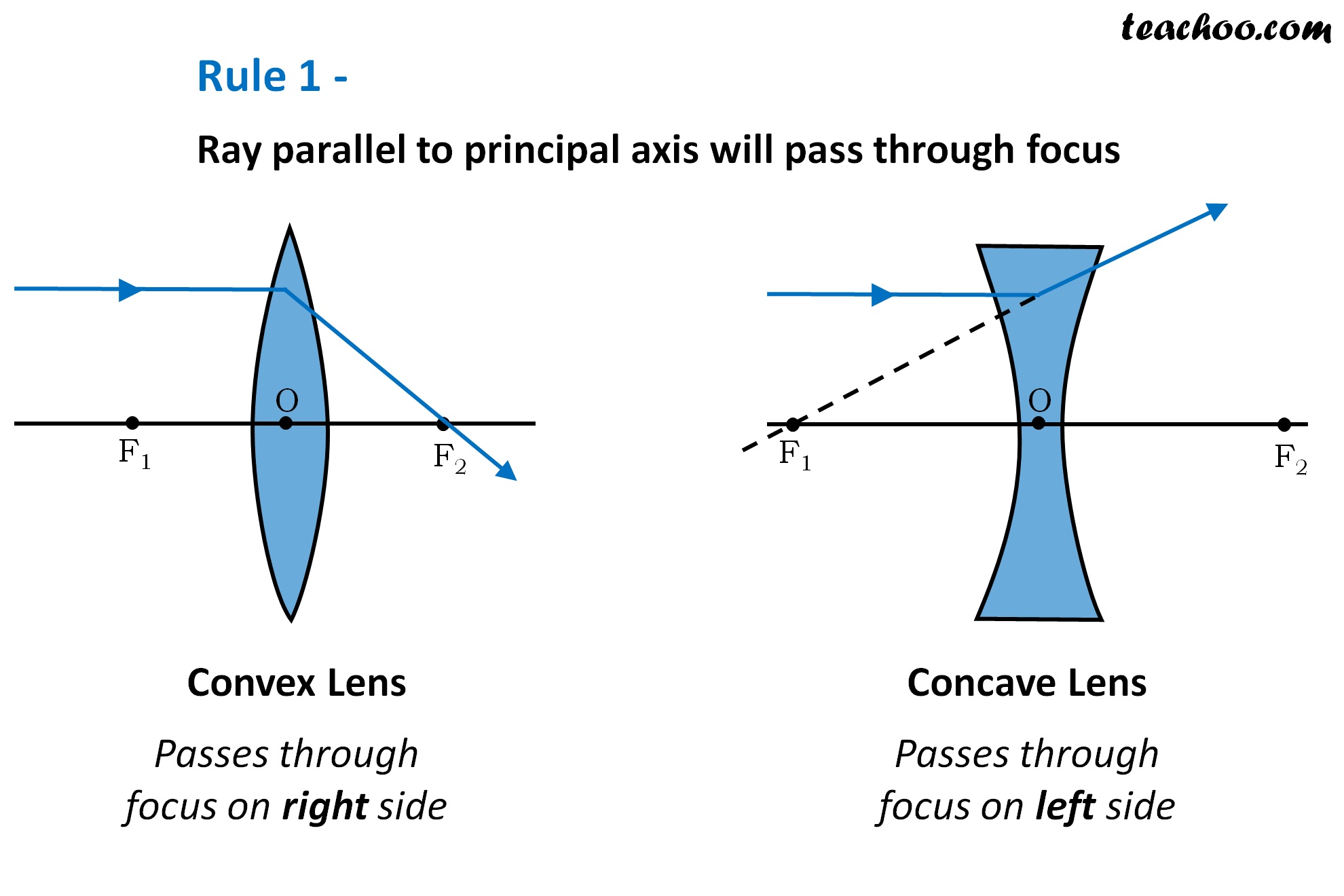
thinner in the center. there are focal points on both sides of each lens. focal length f on both sides is the same. Ray diagram for converging lens. Ray 1 is parallel to the axis and refracts through F. Ray 2 passes through F' before refracting parallel to the axis. Ray 3 passes straight through the center of the lens.

Q 2 Draw a ray diagram showing the diverging action of (i) a convex
A ray approaching a concave converging mirror parallel to its axis is reflected through the focal point F of the mirror on the same side. (See rays 1 and 3 in Figure 2(b).) A ray approaching a convex diverging mirror parallel to its axis is reflected so that it seems to come from the focal point F behind the mirror. (See rays 1 and 3 in Figure 3.)

Concave lens — Science Learning Hub
A concave mirror is a curved mirror that forms a part of a sphere and designed in such a way that rays of light falling on its shiny surface converge upon reflection. Hence, it is also called a converging mirror. A concave mirror produces both real and virtual images, which can be upright or inverted.
Explain the rules of concave and convex mirror
Spherical mirrors may be concave (converging) or convex (diverging). The focal length of a spherical mirror is one-half of its radius of curvature: \(f = \frac{R}{2}\).. If the inside surface is the reflecting surface, it is called a concave mirror. Symmetry is one of the major hallmarks of many optical devices, including mirrors and lenses.

Basic Knowledge of Converging and Diverging Lenses Definition
Physics Optics Concave Convex Mirrors Concave Mirrors and Convex Mirrors A mirror is a surface that reflects almost all incident light. Mirrors come in two types: those with a flat surface, known as plane mirrors, and those with a curved surface, called spherical mirrors.